Sheep is a term for selective grazing animals that may be domesticated (tamed) or wild. This material will primarily focus on domesticated sheep. Behaviorally, sheep are gregarious, precocial, defenseless creatures. But what does that mean? Gregarious means that they flock together or like to be with a group. It is rare to see a sheep by itself because of their gregarious nature. Precocial means that they have a high degree of independence at birth. This means that they can stand on their feet shortly after birth. Sheep are defenseless for the most part against predators like coyotes and wild dogs. Sheep are also very selective in their grazing habits. Sheep have a split in their upper lip, with this they are able to pick the preferred leaves off of the plant.
At one time all sheep were wild. Around 10,000 BC sheep were domesticated by the humans. Most of the wool breeds of sheep were developed from Moulfan sheep. Most of the hair breeds are similar to the Urial sheep of ancient times. Prior to domesticating sheep, the dog and reindeer were domesticated.
As the animals were raised under tamed conditions, they went through several changes. On the outside the sheep began to develop more wool and less hair. The color of the wool and hair changed from brown and shades of brown to whites and blacks. Their ears became more of a lop ear than an erect ear. The horns that the wild sheep possessed were weakened and disappeared from many breeds. On the inside the sheep changed as well. These internal changes happened at both ends. The tails had less vertebrates, or bones than the sheep do now. Today's sheep also have a smaller brain than the sheep 12,000 years ago.
Sheep were tamed for several uses that still apply today. The sheep were first used for meat, skins, milk and wool. Sheep are still used for these basic purposes plus many more. Sheep by-products are in many items that we use everyday.
Sheep Facts
| Animal Profile | ||
| Classification | Scientific Name | Common Term |
| Kingdom | Animalia | animal |
| Phylum | Cordata | vertebrates |
| Class | Mammalia | suckle young |
| Order | Ungulata | hoofed mammals |
| Sub-Order | Artiodactyla | even toed Ungulata |
| Section | Pecora | typical ruminants |
| Family | Bovidae | hollow horned ruminants |
| Subfamily | Caprinac | sheep and goats |
| Genus | Ovis | sheep |
| Species | Ovis Aries | domesticated sheep |
| Sheep Terms | |
| Ram | male of breeding age |
| Wether | castrated male |
| Ram lamb | immature male |
| Ewe lamb | immature female |
| Lamb | newborn |
| Flock | group (3 or more) |
| Tupping | act of breeding |
| Lambing | act of parturition (giving birth) |
| Birth weight | 5 - 8 lb. |
| Average number born | 1.1 - 1.4 lambs/year |
| Weaning age | 2 - 3 months |
| Pasture carrying capacity | 5- 6 ewes and lambs/acre |
| Types of Sheep (body covering) | |
| Fine wool | Merino (100%) |
| Medium wool | 1⁄4, 3⁄8, 1⁄2 blood |
| Long wool | coarse, strong, luster, 12"/year (English breeds) |
| Carpet wool | lowest quality |
| Hair | straight, non elastic and glossy |
| Biological Traits | |||
| Temperature (°F) | Respiration rate | Pulse rate | |
| Maximum | 104.0 | 20 | 80 |
| Average | 102.5 | 16 | 75 |
| Minimum | 102.0 | 10 | 70 |
Life span: 6 -11 years
Chromosome number: 54
| Digestive System | |
| Ruminant | multiple-compartment stomach containing microbes (bugs) that are able to digest forages |
| Daily consumption levels | Food: 2 - 4.5 lbs Water: 0.5 - 1.5 quarts |
| Daily waste volume | Fecal: 2 - 6.5 lbs Urine: 10 - 40 ml per kg of body weight |
| Reproductive Traits | |
| Ewes | |
| Mature weight | 90 - 300 lbs |
| Breeding season | early fall to late winter (some are poly-estrous year round, ex. Dorset) |
| Estrous cycle | 14-19 days seasonally poly-estrous |
| Duration of estrous | 24 - 26 hours (standing heat) |
| Time of ovulation | 24-30 hours from beginning of estrous |
| Gestation period | 145 - 155 days |
| Breeding/year | 1 - 2/year |
| Artificial insemination | Yes, cervical or vaginal method Intrauterine method |
| Ewe lambs | |
| Puberty | 5 - 8 months (80-100 lbs) |
| Minimum breeding age | 8 - 10 months |
| Rams | |
| Puberty | 6 - 8 months |
| Mature weight | 150 - 450 lbs |
| Serviceability | 1 ram: 30 - 35 ewes (60 day breeding season) |
| Ejaculate volume | 0.8 - 1.2 ml |
| Sperm concentration | 2,000 - 3,000 million/ml |
| Motile sperm | 60 - 80 % |
| Semen freezable | yes |
| Under the Hide (Carcass Information) | |||
| High | Average | Low | |
| Age at slaughter | 8 months | 6 months | 4 months |
| Live weight | 160 lbs | 125 lbs | 85 lbs |
| Dressing percentage (%) | 57% | 52% | 45% |
| Fat thickness | .50 in | .25 in | .05 in |
| Kidney, pelvic, and heart fat (% KPH) | 6.0% | 3.0% | 1.5% |
Yield Grades
1, 2, 3, 4 & 5, based on the backfat thickness at the 12th rib
yield grade formula = 0.4 + (10 x adjusted back fat thickness, inches)
Quality Grades
Based on a composite evaluation of conformation, maturity, and quality of the lean flesh
- US Prime
- US Choice
- US Good
- US Utility
Degrees of flank fat streaking - used to predict marbling, since lamb carcasses are not ribbed to expose ribeye muscle marbling
- Devoid
- Practically devoid
- Traces
- Slight
- Small
- Modest
- Moderate
- Slightly abundant
- Moderately abundant
- Abundant
Maturity (physiological) - Chronological age of the live lamb is determined by assessing the physiological age of the bone and muscle. Maturity grades are A and B.
Break joint (young lambs) - the rigid surface of the joint is quite red, moist, and porous
Spool joint (older sheep) - the joints become drier and harder
Color of lean - red to dark red
- 20 temporary teeth
- 32 permanent teeth at maturity
- 4 pairs of incisor teeth on lower jaw
- upper incisors missing
- cartilaginous (hard) dental pad on upper jaw
- split upper lip with mobile lips
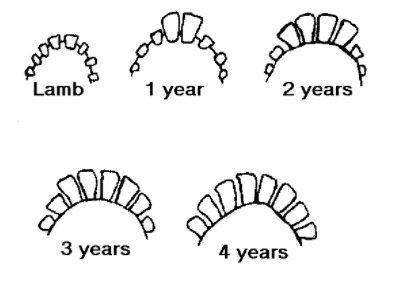
| Age of Sheep (teeth) | |
| Lamb | 4 pair of incisors |
| 1 year | middle pair of incisors |
| 2 years | 2nd pair of permanent incisors |
| 3 years | 3rd pair of permanent incisors |
| 4 years | 4th pair of permanent incisors |
| 5 years | all permanent incisors close together |
| 6 years | incisors begin spreading apart |
| 7-8 years | some incisors broken |
| 10-12 years | all incisors missing |
Publication date: March 24, 2003
N.C. Cooperative Extension prohibits discrimination and harassment regardless of age, color, disability, family and marital status, gender identity, national origin, political beliefs, race, religion, sex (including pregnancy), sexual orientation and veteran status.