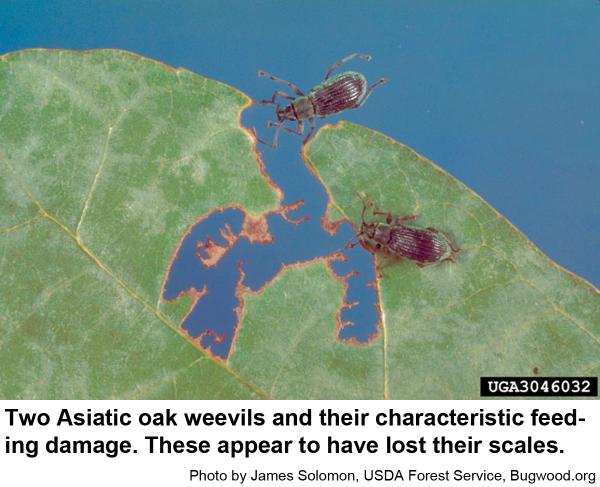
Descrition and Biology
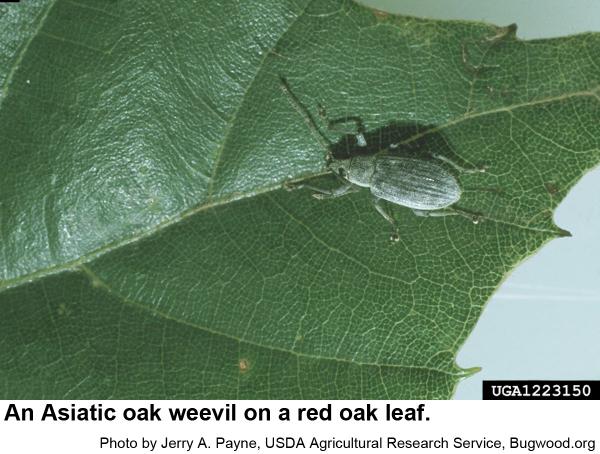
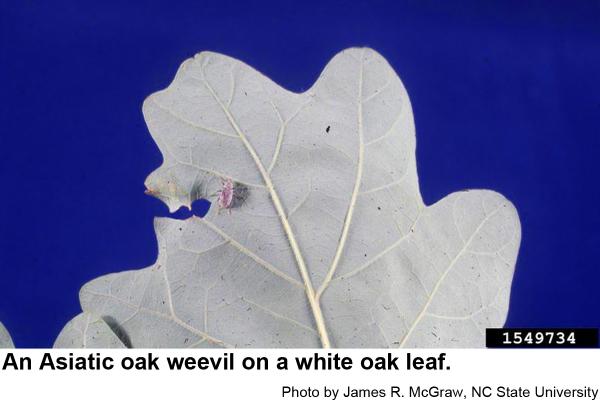
The Asiatic oak weevil, Cyrtepistomus castaneus, is a small (1/4 to 1/3 inch long), broadnosed weevil. It is usually greenish-gray although if its scales are worn away, some appear reddish-brown. It was introduced into the United States in 1933 (New Jersey) and now occurs throughout much of the eastern US. Small, legless grubs associated with the roots of hardwood trees survive the fall, winter, and early spring. The grubs pupate and new adults emerge during the spring to feed on the leaves of oaks and chestnut. Asiatic oak weevils emerge in May and become most abundant in late June and early July. They feed on the margins of leaves, sometimes devouring everything but the main veins. This weevil takes shelter in leaves tied together by caterpillars. The weevils start laying eggs in soil in July and continue on into early fall. Asiatic oak weevils are sometimes a household pest because they invade houses apparently for hibernation quarters.
Host Plants
Asiatic oak weevils feed primarily on oaks and chestnut although they have been reported from other woody plants. Adults fed red oak and black oak leaves lived longer and laid significantly more eggs than weevils fed white oak or sugar maple
Residential Recommendations
The Asiatic oak weevil likely has not developed resistance to insecticides. If a specimen tree is small enough to spray, and if the tree is heavily infested, just about any insecticide labeled for landscape use should give adequate control.
Other References
- Abundance and frequency of the Asiatic oak weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and defoliation on American, Chinese, and hybrid chestnut (Castanea). Case, A. E. et al. 2016. Journal of Insect Science.
- Impacts of the Asiatic oak weevil (Cyrtepistomus castaneus) on the growth and survivorship of black oak (Quercus velutina) seedlings. Marquis, R. and L. B. Catano. No Date. Washington University in St. Louis.
- Species Cyrtepistomus castaneus - Asiatic Oak Weevil. Elliot L. et al. 2013 (update). Iowa State University Department of Entomology.
- Extension Plant Pathology Publications and Factsheets
- Horticultural Science Publications
- North Carolina Agricultural Chemicals Manual
For assistance with a specific problem, contact your local N.C. Cooperative Extension Center.
This Factsheet has not been peer reviewed.
Publication date: July 23, 2019
Reviewed/Revised: May 3, 2024
Recommendations for the use of agricultural chemicals are included in this publication as a convenience to the reader. The use of brand names and any mention or listing of commercial products or services in this publication does not imply endorsement by NC State University or N.C. A&T State University nor discrimination against similar products or services not mentioned. Individuals who use agricultural chemicals are responsible for ensuring that the intended use complies with current regulations and conforms to the product label. Be sure to obtain current information about usage regulations and examine a current product label before applying any chemical. For assistance, contact your local N.C. Cooperative Extension county center.
N.C. Cooperative Extension prohibits discrimination and harassment regardless of age, color, disability, family and marital status, gender identity, national origin, political beliefs, race, religion, sex (including pregnancy), sexual orientation and veteran status.