Description and Biology
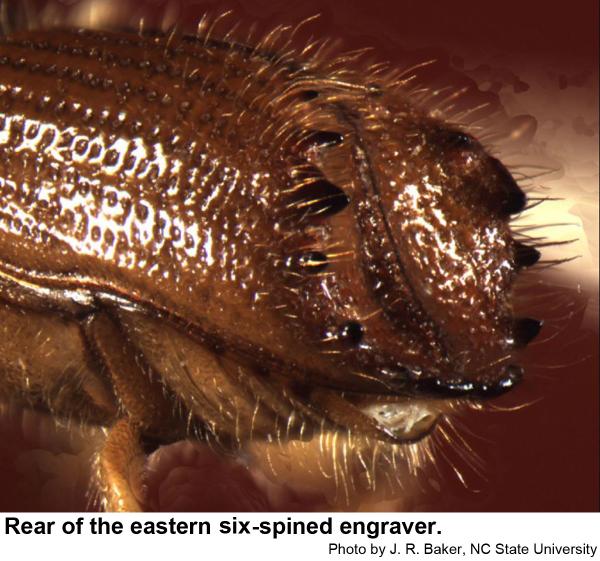
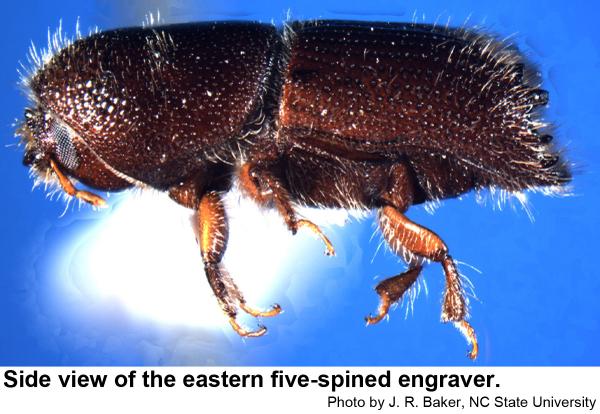
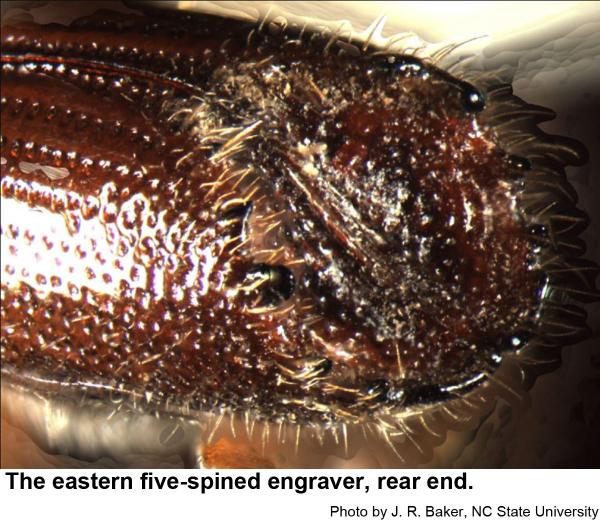
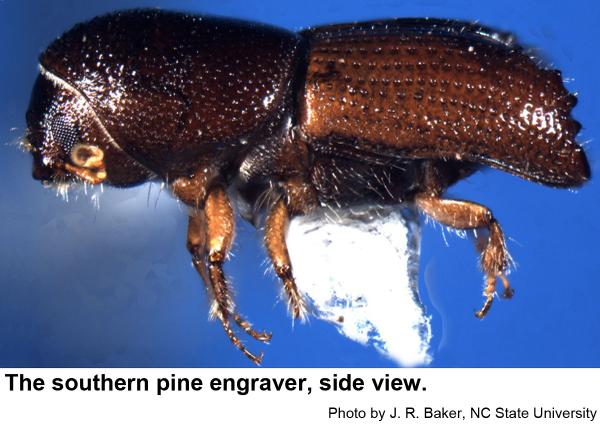
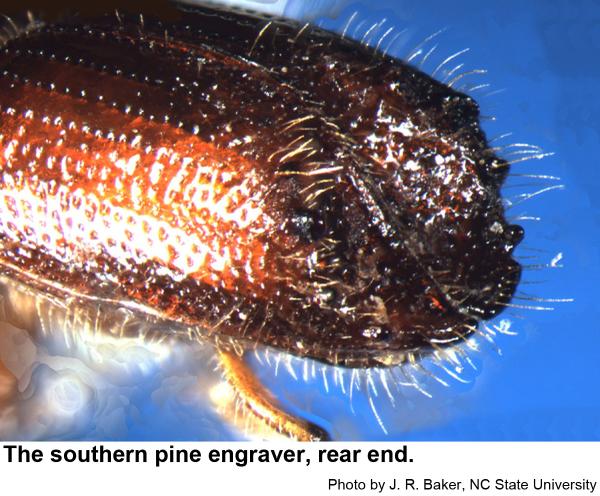
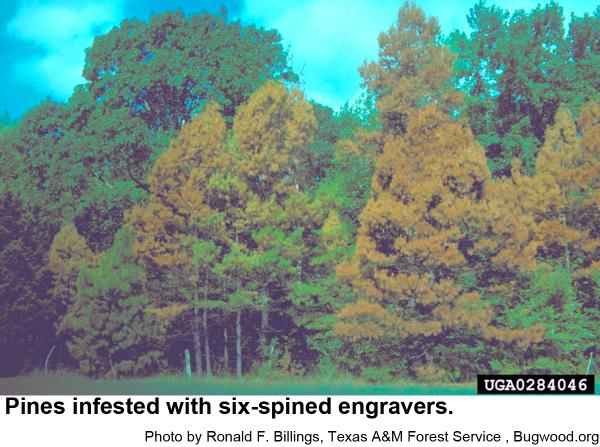
Our three species of pine engraver beetles are in the genus Ips. They prefer to breed in fallen trees and slash left behind in logging, but they sometimes infest apparently healthy trees especially after droughts or injury. Spots of infested trees are likely to increase in size during droughts. Pine engravers are dark red brown to almost black. The end of the wings looks as if they has been cut off at an angle and slightly hollowed out. Adults have six (eastern six-spined engraver, Ips calligraphus), five (eastern five-spined engraver, Ips grandicollis ), or four (southern pine engraver, Ips avulsus) bumps or spines on either outer edge of the hollow.
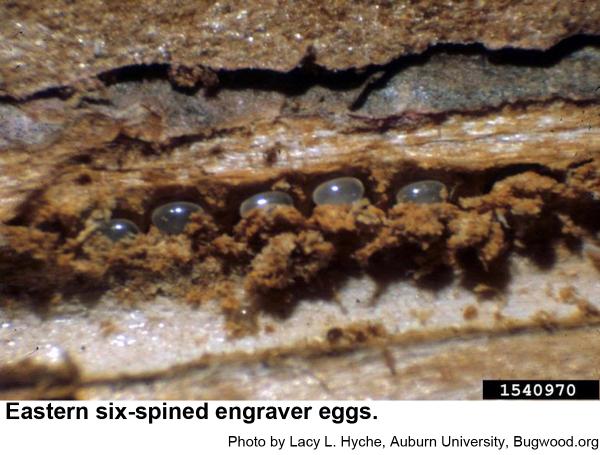
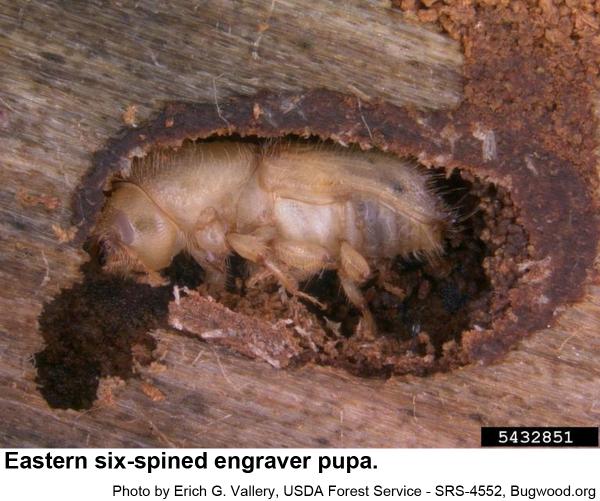
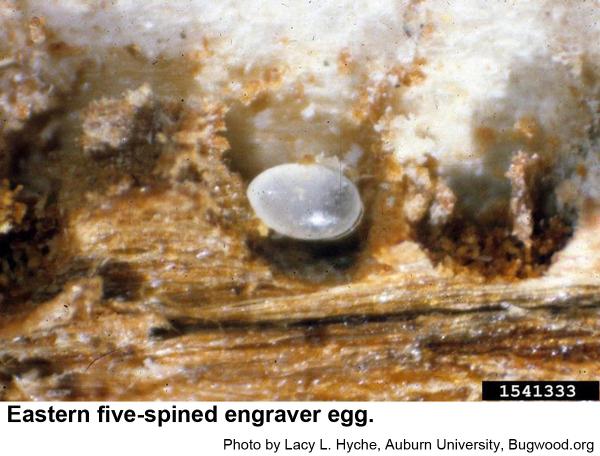
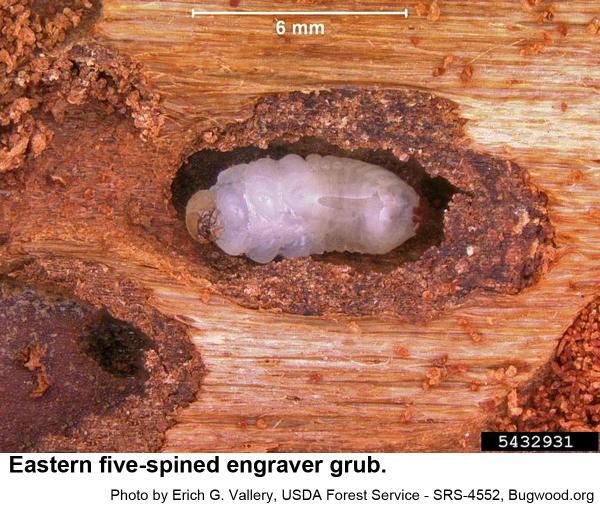
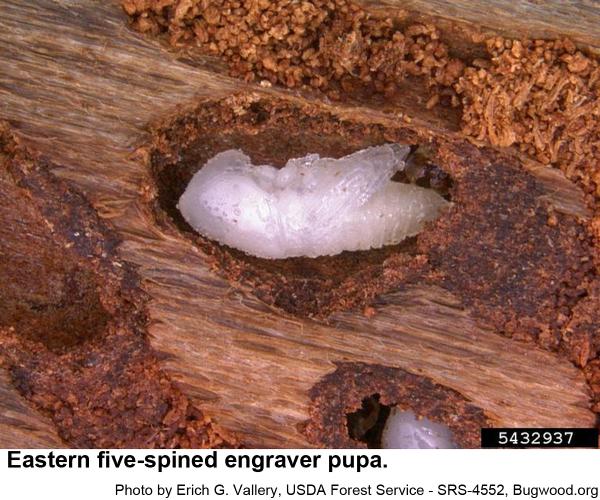
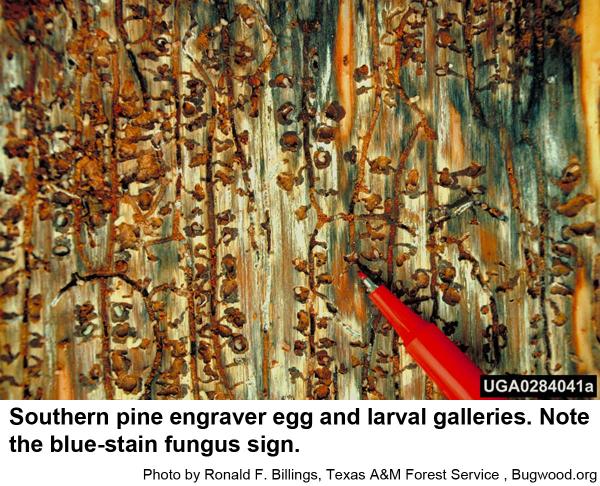
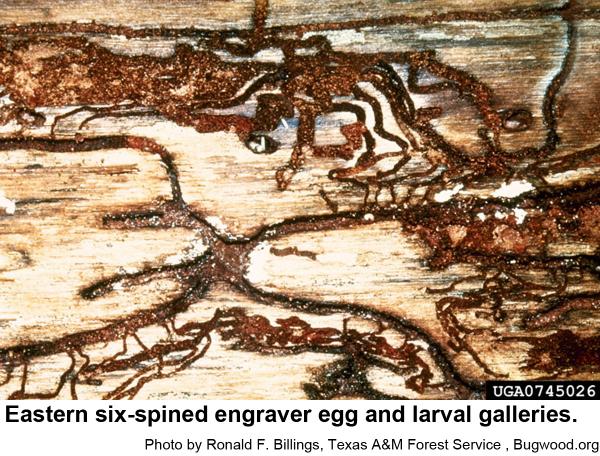
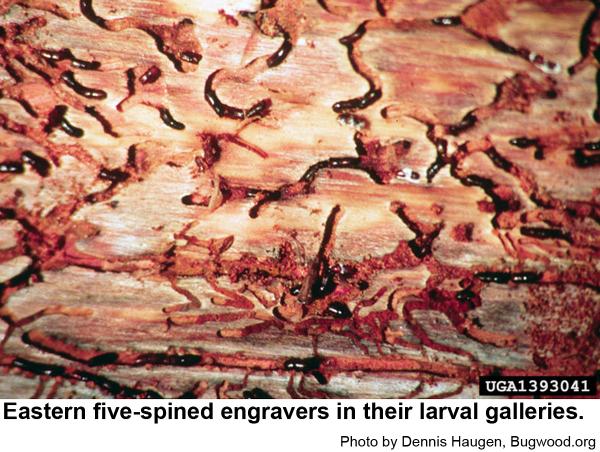
Male engravers usually initiate attacks pines or logging debris by boring an entrance tunnel through the outer bark and excavating a small, irregular "nuptial chamber." One to four females are attracted to the the chamber, where mating occurs. From this chamber, each female then begins constructing Y or H-shaped egg galleries. Grubs soon hatch and chew tunnels in the inner bark as they grow. When mature, grubs pupate and soon another generation of engravers emerges to feed on bluestain fungal spores before they chew through the bark to continue their existence. In hot weather, development may be as short as 3 weeks. The overwintering generation develops several months longer.
Eastern six-spined engravers are 3/16 inch long. Their eggs are oblong, pearly white, and very small. The grub-like larvae are small, whitish, and legless, and have orange-brown heads. Eastern six-spined engraver pupae are waxy white at first and about 3/16 inch long. Eastern six-spined engravers commonly infest thick-barked pines more than 4 inches in diameter.
Eastern five-spined engravers are a little over 1/8 inch long. Their eggs are very small, and their grubs are small, whitish, and legless with orange-brown heads. Pupae are waxy white at first and about 1/8 inch long. Recently felled trees and fresh logging debris are favored breeding material. In standing trees, this species usually infests upper trunks and bases of large branches.
Southern pine engravers are about 1/8 inch long. The wing covers are lighter brown than the thorax. The eggs very small and their grubs are small, whitish, and legless with orange-brown heads. Pupae are waxy white at first and about 1/8 inch long Fresh, thin-barked logging debris, such as the upper portions of branches and tops of pines, is often infested. The crowns of large, living trees may be attacked and stunted or completely killed. It is common to find more than one pine engraver, as well as other pine-infesting beetles, infesting parts of the same tree.
Host Plants
All of our native pines are susceptible to pine engraver beetles. Spot or groups killing of trees often happens. Infested trees are usually infested with blue stain fungi (Ceratocystis pini and other fungi) that themselves are usually be fatal to pines. Often, the first sign of attack is yellowing or reddening of needles in tree crowns. By this time most of the beetles have completed their life cycle and emerged from the tree.
Residential Recommendations
They pyrethroid insecticides permethrin and bifenthrin are labeled for bark beetle control. When used as directed, pyrethroids are very toxic to insects but are not particularly hazardous to humans and pets (other than fish—avoid using pyrethroids around pools, ponds, and streams). Unfortunately, pine engraver infestations may occur high in a tree on the leader and topmost branches where it may be difficult to spray with equipment available to homeowners. Not only that, but by the time pine engravers are discovered in a tree, it is highly likely that the tree is doomed. Cultural control of engravers consists of cutting down infested trees and debarking them and burning or burying the slash.
Other Resources
- Ips Bark Beetles in the South. Conner, M. D. and R. C. Wilkinson. 1983. U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service. Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 129. 8pp.
- Pine engraver beetle, Ips pini (Say) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae [formerly Scolytidae]). R. G. Van Driesche al. No date.
Forest Pest Insects in North America: a Photographic Guide. - Pine Ips Species (Engraver Beetles), Attracted to green slash. Anonymous. 2011. Forest Health Protection, Rocky Mountain.
- Extension Plant Pathology Publications and Factsheets
- Horticultural Science Publications
- North Carolina Agricultural Chemicals Manual
For assistance with a specific problem, contact your local N.C. Cooperative Extension Center
Publication date: Aug. 10, 2019
Reviewed/Revised: May 15, 2024
Recommendations for the use of agricultural chemicals are included in this publication as a convenience to the reader. The use of brand names and any mention or listing of commercial products or services in this publication does not imply endorsement by NC State University or N.C. A&T State University nor discrimination against similar products or services not mentioned. Individuals who use agricultural chemicals are responsible for ensuring that the intended use complies with current regulations and conforms to the product label. Be sure to obtain current information about usage regulations and examine a current product label before applying any chemical. For assistance, contact your local N.C. Cooperative Extension county center.
N.C. Cooperative Extension prohibits discrimination and harassment regardless of age, color, disability, family and marital status, gender identity, national origin, political beliefs, race, religion, sex (including pregnancy), sexual orientation and veteran status.