Introduction
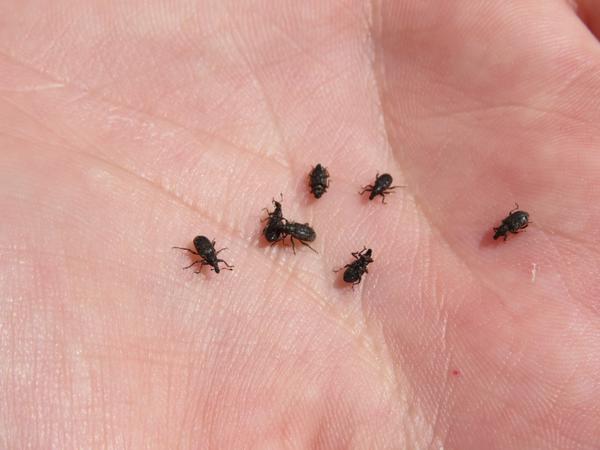
Initially identified as the Hyperodes weevil, the annual bluegrass weevil, Listronotus maculicollis, has been historically a destructive pest of annual bluegrass and creeping bentgrass on fairways and greens in the northeastern United States. Since first described as a turfgrass pest in Connecticut in 1931, it has spread south and west and has become an insect of concern for managers in western North Carolina (Figure 1).
Description
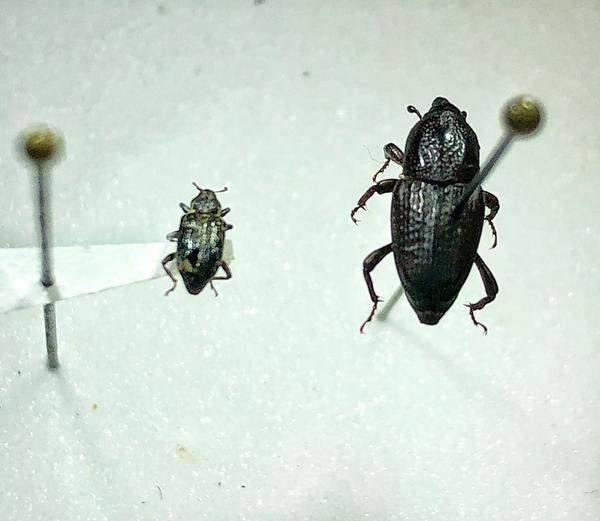
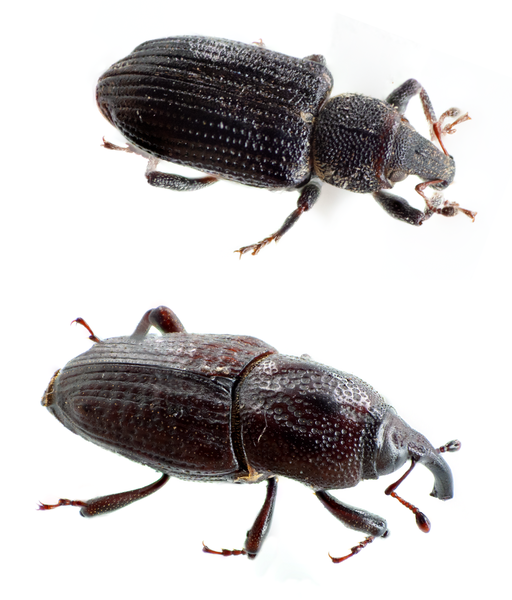
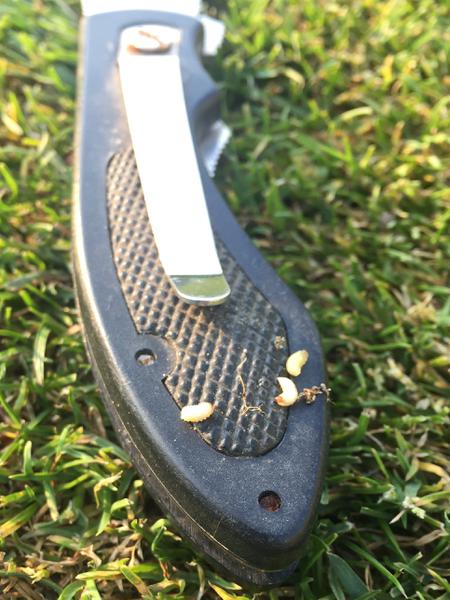
Annual bluegrass weevil adults (Figure 2) are dark brown or black beetles, approximately 1⁄8-in long with a pronounced, curved snout and have gray-yellow hairs and scales on the thorax and elytra (hind wings). ABWs resemble billbugs (Figure 3), another common turfgrass pest, but are much smaller (~1⁄3 size), their antennae attach to the tip of their proboscis (snout), rather than the base and their snout is shorter and stouter than that of a billbug (Figure 4). Larvae are cream-colored with red-brown head capsules, legless, and range from 1⁄25 to 1⁄6 inches long (Figure 5). ABW eggs are yellow initially but turn gray as they mature.
Pest Status
In North Carolina, annual bluegrass weevils are primarily a pest of Poa annua and creeping bentgrass but can also feed on perennial ryegrass.
Biology
In North Carolina, annual bluegrass weeil adults overwinter primarily in golf course fairways, collars and approaches. Although research from the NE US indicates annual bluegrass weevil adults overwinter in treelines and other semi-protected areas on golf courses, we have not observed spring migration from these types of dedicated overwintering sites in NC. Overwintered adults become active February-May and females lay 2-3 eggs in leaf sheaths, typically in short-mown turf. Larvae emerge in April-June, depending on location, and develop through five instars that typically last 5-7 days each before pupating. Pupae develop for another 5-7 days before adults emerge, with the first peaks in adult activity usually occurring in early-mid May. In North Carolina, ABWs have three generations per year.
Although there are some similarities in terms of ABW behavior in the northeast and the southeast, we have observed considerable differences in terms of life stage appearance timings. Adults in North Carolina appear and are active much earlier than in the northeastern US. Once overwintered adults have emerged, ABWs quickly cycle through three generations and most ABW activity has ceased by October. As a result, the ABW season in North Carolina is more condensed and occurs earlier in the year. This can have a tremendous impact on insecticide selection and application timing for management of this pest.
Damage
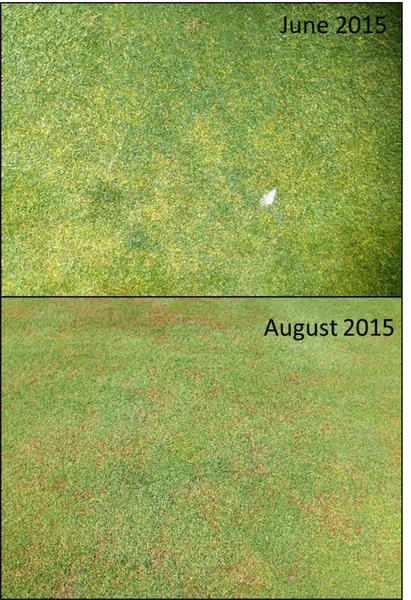
As temperatures increase in late spring, adult annual bluegrass weevils feed, mate, and lay eggs in the turfgrass. Adults cause damage to the turfgrass plant by chewing tiny notches in blades and although previous research has stated that this does not appear to have a detrimental effect on the overall health of the turf stand, we have observed noticeable turf damage coinciding with increases in adult activity. Larval feeding consists of tiny larvae feeding within the grass stem. As they grow, they move down around the outside of the plant and into the crown. Larval damage causes small, yellow spots on short-mown turf. Early damage typically occurs in mid-May. More significant damage is observed when there is an overlap between the previous generation’s adult population and the next generation’s larval population (early-mid July and early-mid August) (Figure 6).
Monitoring
To sample for annual bluegrass weevil adults, apply a soapy water flush (1-2 tablespoons per 1 gallon water) to a square section of the turf (2 feet x 2 feet) and wait 3-4 minutes for adults to emerge. To examine a turf stand for larvae, cut a small sample (3 inches x 3 inches x 3 inches) section from the area. Tease the tissue apart and look for all life stages. Submerge the sample in a salt-water solution (3⁄4 cup salt in 1 quart of water) for one hour. In North Carolina, larvae are generally recovered from areas of moderate to severe damage but are difficult to find with random sampling.
Control
Biological Control
Some research (Vittum 1999) has shown that the beneficial nematode Steinernema carpocapsae can reduce annual bluegrass weevil populations by almost 50%. Bt can also reduce larval populations by 50-65% (Vittum 2005). Spinosad can also be very effective (80% control) against larvae but only when used at a high rate. As with all control options, accurate timing is essential to successfully reducing populations.
Chemical Control
Pyrethroids (bifenthrin, lambda-cyhalothrin) are most effective against ABW adults while anthranilic diamides (chlorantraniliprole, cyantraniliprole, tetraniliprole) and an insect growth regulator (novaluron) are more effective against the larvae. Each of these insecticides may be used in a control program to target different life stages. Pyrethroid applications targeting adults should be timed when adult activity peaks.
Similar to other multivoltine insects in turfgrass, such as chinch bugs, repeated applications throughout the year can result in resistance issues if managers do not rotate insecticide classes. Resistance in ABW resulting in field control failures can build in as short as five years when the same mode of action is used exclusively and repeatedly. Once resistance has been established, the use of the pesticide that led to resistance is ineffective and can no longer be used. Furthermore, pyrethroid resistance can also lead to reduced efficacy in other insecticide classes by as much as 57% (Koppenhöfer et al. 2012) For control of ABW, pyrethroid resistance is the greatest management concern as they provide the highest and most consistent level of adult control.
| Insecticide and Formulation | Amount per 1,000 sq ft | Precaution and Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| bifenthrin (Menace, Talstar, others) F, GC | 0.25-0.5 fl oz | Monitor for adults, apply at peak activity; use GC formulation for golf courses |
| chlorantraniliprole (Acelepryn) | 0.28 fl oz | Apply appoximately 7-14 days after adulticide to target larvae |
| cyantraniliprole (Ference) | 0.28 fl oz | Monitor for adults, apply at peak activity, apply appoximately 7-14 days after adulticide to target larvae |
| indoxacarb (Provaunt) | 0.28 fl oz | Monitor for adults, apply at peak activity, apply appoximately 7-14 days after adulticide to target larvae |
| lambda-cyhalothrin (Battle, Scimitar, Cyonara) | 0.23 fl oz | Monitor for adults, apply at peak activity |
| novaluron (Suprado) | 2-2.3 fl oz | Apply approximately 7 to 14 days after adult emergence to target larvae. |
| Spinosad (Conserve SC) | 1.2 fl oz | Monitor for adults, apply at peak activity. |
| Tetraniliprole (Tetrino) | 0.367-0.735 fl oz | Apply approximately 7 to 14 days after adult emergence to target larvae. |
|
zeta-cypermethrin, bifenthrin, and imidacloprid (Triple Crown) |
0.57-0.8 fl oz | Monitor for adults, apply at peak activity. |
ABW IPM Recommendation
Monitoring for annual bluegrass weevil is an essential part of a successful management program, particularly in North Carolina. Because this insect is not fully established in some areas, when sampling at sites that are relatively close to each other (< 15 miles apart), you may notice a big difference in emergence timing, population size of ABW life stages, and damage intensity. Therefore, proximity to a golf course that may or may not be spraying for ABW should not dictate the application timing for a nearby site. Depending on where you are located, insecticide application timings may need to be adjusted by a week or two in order to maximize product efficacy. Keep a map of areas of past damage, apply a soapy water flush to these areas weekly, and keep track of adult numbers over the growing season. When these numbers start to increase, plan your application approach and select the most effective product for that life stage.
References
Annual bluegrass weevil: a metropolitan nightmare. Vittum, P. J. 1999. Turfgrass Trends 8 (5): 1-6.
Biology and Control of the Annual Bluegrass Weevil. Koppenhöfer, A. and B. McGraw. 2016.
Evaluation of Insecticides on Hyperodes spp, a pest of annual bluegrass turf (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Tashiro, H., et al. 1977. Journal of Economic Entomology 70: 729-733.
Seasonal Activity of Listronotus maculicollis (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) on Annual Bluegrass. Vittum, P. J., and H. Tashiro. 1987. Journal of Economic Entomology 80: 773-778. https://ncturfbugs.wordpress.ncsu.edu/homepage/
Turfgrass Insects of the United States and Canada, 2nd ed. Vittum, P.J., M.G.Villani, and H. Tashiro. 1999. Cornell University Press, NY. 422pp.
Vittum, P. 2005. Annual bluegrass weevil: A metropolitan pest on the move. Golf Course Management. May 2005. p 105-108.
- 2018 Pest Control for Professional Turfgrass Managers. Bowman, D. et al. 2017. NC State Extension Publication AG-408. 81 pp.
- Extension Plant Pathology Publications and Factsheets
- Horticultural Science Publications
- North Carolina Agricultural Chemicals Manual
For assistance with a specific problem, contact your local Cooperative Extension Center
Publication date: Oct. 25, 2017
Reviewed/Revised: Aug. 31, 2022
Recommendations for the use of agricultural chemicals are included in this publication as a convenience to the reader. The use of brand names and any mention or listing of commercial products or services in this publication does not imply endorsement by NC State University or N.C. A&T State University nor discrimination against similar products or services not mentioned. Individuals who use agricultural chemicals are responsible for ensuring that the intended use complies with current regulations and conforms to the product label. Be sure to obtain current information about usage regulations and examine a current product label before applying any chemical. For assistance, contact your local N.C. Cooperative Extension county center.
N.C. Cooperative Extension prohibits discrimination and harassment regardless of age, color, disability, family and marital status, gender identity, national origin, political beliefs, race, religion, sex (including pregnancy), sexual orientation and veteran status.