Description and Biology
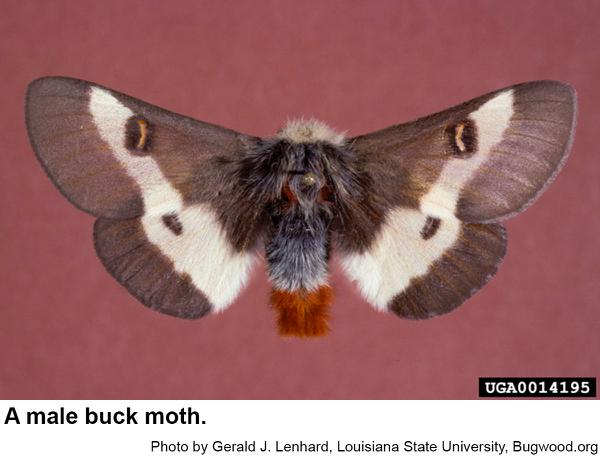
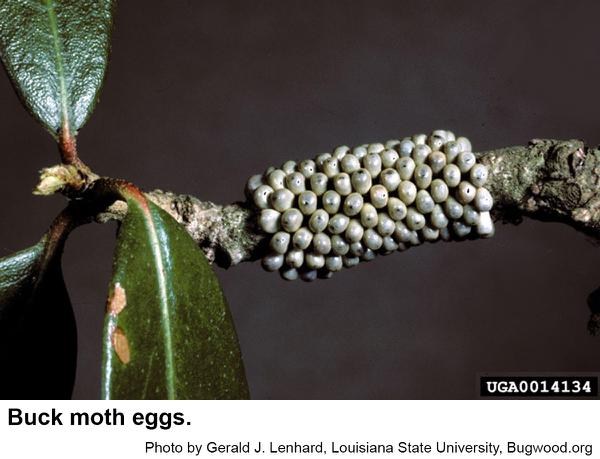
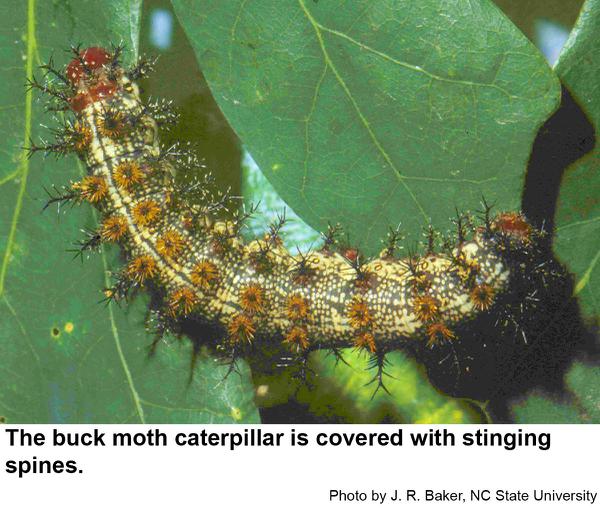
Buck moths, Hemileuca maia, are so called because they fly during the day during deer season. Other species of moths usually don't fly during the day. Buck moths are in the family of the giant silkworms but differ from the others in that the female moths lay their eggs in the fall for next year's crop of caterpillars. Eggs are laid in a tight mass around an oak twig. The rest of the giant silkworm moths emerge in the spring and summer and lay eggs from which caterpillars hatch in only a few days. A third difference is that buck moth caterpillars have stinging hairs that can cause a severely painful reaction to folks who are sensitive to the urticating fluid contained in the hairs. With some folks these stings may require medical attention. Buck moths are dark gray to black with a conspicuous white band on each wing. Each band has a noticeable eyespot. The wingspan is 2 to 3 inches (males are smaller than females). The tip of male moths is rusty red. Moths emerge in the morning and mate in early afternoon. Winter is spent as eggs that hatch the following spring. Young caterpillars feed in groups. Older buck moth caterpillars are black and spiny although they may be covered with tiny white spots to the point that they appear almost white. The spines are grouped on bumps arranged in multiple rows along the body. The spines on top are longer and more branched. These caterpillars grow to almost 2 ½ inches long. Mature caterpillars crawl down and seek shelter in leaf litter or a few inches underground if the soil is soft enough. Then caterpillars molt into pupae and moths emerge from the pupal skins from September through December, although some may not emerge for a year or two. We have only one generation per year.
Host Plants
Buck moth caterpillars feed primarily on oaks including scrub oak, live oak, blackjack oak, and dwarf chestnut oak. Buck moths do not feed.
Residential Recommendations
Buck moth caterpillars are not particularly resistant to pesticides. Bacillus thuringiensis (on young caterpillars), Sevin, or some other properly labeled insecticide should give more than adequate control.
Buck moth caterpillar stings cause immediate pain that then spreads to nearby lymph nodes. Swelling and redness can last over a week. Wash the site immediately to remove any loose spines and allow it to air dry. Any remaining spines can then be removed with an adhesive such as duct tape. Not handling caterpillars that have spines is one of the best ways to avoid receiving stings.
References
- Eastern buckmoth, Hemileuca maia (Drury, 1773). Anonymous. 2010 (after). Butterflies and Moths of North America.
- Common name: buck moth, scientific name: Hemileuca maia (Drury) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Saturniidae: Hemileucinae). Scott, C. and P. E. Kaufman. 2015 (reviewed). Featured Creatures, Entomology & Nematology, FDACS/DPI, EDIS. Publication Number: EENY-464.
- Extension Plant Pathology Publications and Factsheets
- Horticultural Science Publications
- North Carolina Agricultural Chemicals Manual
For assistance with a specific problem, contact your local Cooperative Extension Center
This Factsheet has not been peer reviewed.
Publication date: Jan. 25, 2017
Revised: Sept. 11, 2019
Recommendations for the use of agricultural chemicals are included in this publication as a convenience to the reader. The use of brand names and any mention or listing of commercial products or services in this publication does not imply endorsement by NC State University or N.C. A&T State University nor discrimination against similar products or services not mentioned. Individuals who use agricultural chemicals are responsible for ensuring that the intended use complies with current regulations and conforms to the product label. Be sure to obtain current information about usage regulations and examine a current product label before applying any chemical. For assistance, contact your local N.C. Cooperative Extension county center.
N.C. Cooperative Extension prohibits discrimination and harassment regardless of age, color, disability, family and marital status, gender identity, national origin, political beliefs, race, religion, sex (including pregnancy), sexual orientation and veteran status.