Description and Biology
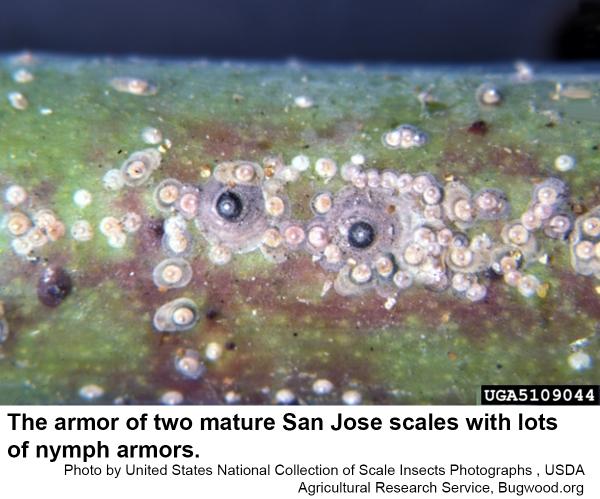
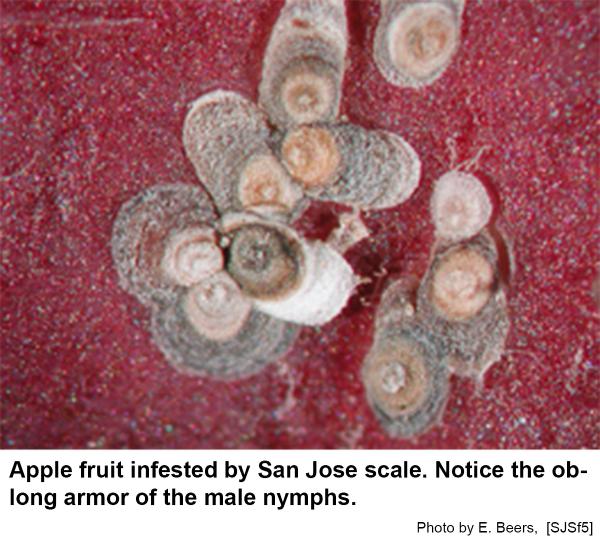
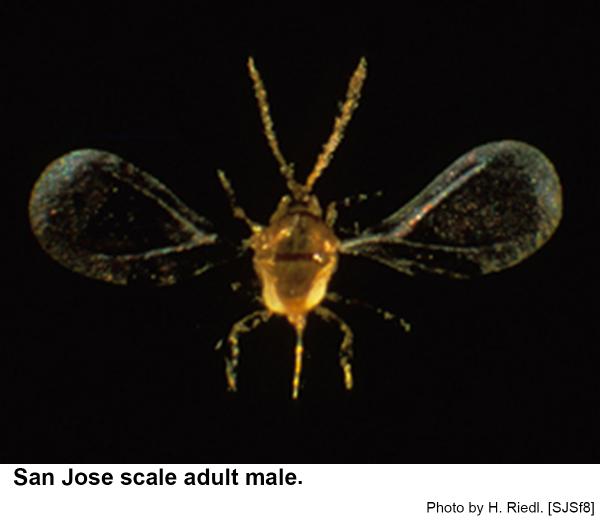
The San Jose scale, Quadraspidiotus perniciosus, is one of the armored scale insects that has given fruit growers a fit over the years. Male San Jose scales have armor that is oblong, with a small black spot near one end, and is much smaller than the female. Very young females have round, nearly white armor that turns dark gray as they mature. There is usually a black spot in the center of the armor. Females are yellow with a wide teardrop shape. Males are tiny, two-winged gnat-like insects. For six weeks, females give birth to approximately 400 tiny, lemon yellow crawlers that move around in search of a suitable place to settle. After they settle, crawlers secrete a waxy substance that produces a grayish-yellow scale covering which becomes darker with age. Males mature in 25 days and female mature in 31 days. This scale overwinters as nymphs under a small, round, black armor. The first generation of females matures when apples are in bloom, and the males emerge and mate at petal fall. First-generation crawlers begin appearing in early June. These crawlers develop into mature adults by late July. Second-generation adults appear from late July to early September; and, if a third generation occurs, it appears in late October to early November. The life cycle is completed in about 37 days. Crawlers can usually be found from early June until a hard frost in the fall.
Host Plants
San Jose scale is destructive on apple, cherry, peach, pear, prune and other tree fruits. It also attacks nut trees, berry bushes and many kinds of shade trees and ornamental shrubs. As the scale feeds, it injects its saliva into the tree. This results in decline and possible death of the whole plant if parasites and diseases of the scale fail to reduce the scale population. Scales on new growth twigs, leaves, and fruit cause a deep purplish-red spots. Prolonged attack causes cracking and splitting of the wood; if the scale is not controlled, the tree or shrub may die.
Residential Recommendation
The specific name of this pest, perniciosus, indicates how harmful it is and how difficult it is to control. Fortunately, horticultural oils should give adequate control of the San Jose scale. Oil can be applied before new growth starts in the spring at 4% (that is 10 tablespoons per gallon of water) or during the growing season at 2% (5 tablespoons per gallon). These oils should be available at most garden centers, nurseries, and big box store garden areas. In the growing season, plants should be sprayed at least twice (two weeks in between) and again before bud break the next January or February.
References
- Armored Scale Identification and Management on Ornamental Plants. Frank, S. 2010. Entomology Insect Notes, NC State Extension Publications.
- San Jose Scale. Krawczyk, G. No Date. Tree Fruit Production. PennState Extension. Tree Fruit Insect and Mite Pest Fact Sheets.
- San Jose Scale Management in North Carolina Peaches. Walgenbach, J. No Date. NC State University.
- Orchard IPM - BMSB and San Jose Scale. Biddinger, D. no date. Penn State Extension.
- San Jose Scale. Walgenbach, J. 2015. NC State Extension Publications.
- NC State Extension Plant Pathology Publications
- NC State Horticultural Science Publications
- North Carolina Agricultural Chemicals Manual
For assistance with a specific problem, contact your local Cooperative Extension center.
This Factsheet has not been peer reviewed.
Publication date: May 17, 2016
Reviewed/Revised: Oct. 9, 2019
Recommendations for the use of agricultural chemicals are included in this publication as a convenience to the reader. The use of brand names and any mention or listing of commercial products or services in this publication does not imply endorsement by NC State University or N.C. A&T State University nor discrimination against similar products or services not mentioned. Individuals who use agricultural chemicals are responsible for ensuring that the intended use complies with current regulations and conforms to the product label. Be sure to obtain current information about usage regulations and examine a current product label before applying any chemical. For assistance, contact your local N.C. Cooperative Extension county center.
N.C. Cooperative Extension prohibits discrimination and harassment regardless of age, color, disability, family and marital status, gender identity, national origin, political beliefs, race, religion, sex (including pregnancy), sexual orientation and veteran status.